How do sensory cortical dynamics contribute to distractor attenuation ?
When performing goal-directed tasks, one major challenge is ignoring all the distracting stimuli in our environment and staying focused on the task at hand, however current knowledge of how neural circuits overcome susceptibility to distracting stimuli is limited. Using a novel distractor task design in mice, we found that vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) modulation accompanied distractor attenuation. Using cutting-edge in vivo calcium imaging, optogenetic tools, genetic mouse models and intersectional strategies, and machine learning, we are examining the causal link between anterior cingulate cortex to vasoactive intestinal peptide neurons in V1 in overcoming a distractor challenge.
Mouse performing a visual discrimination task in the presence of auditory distractors
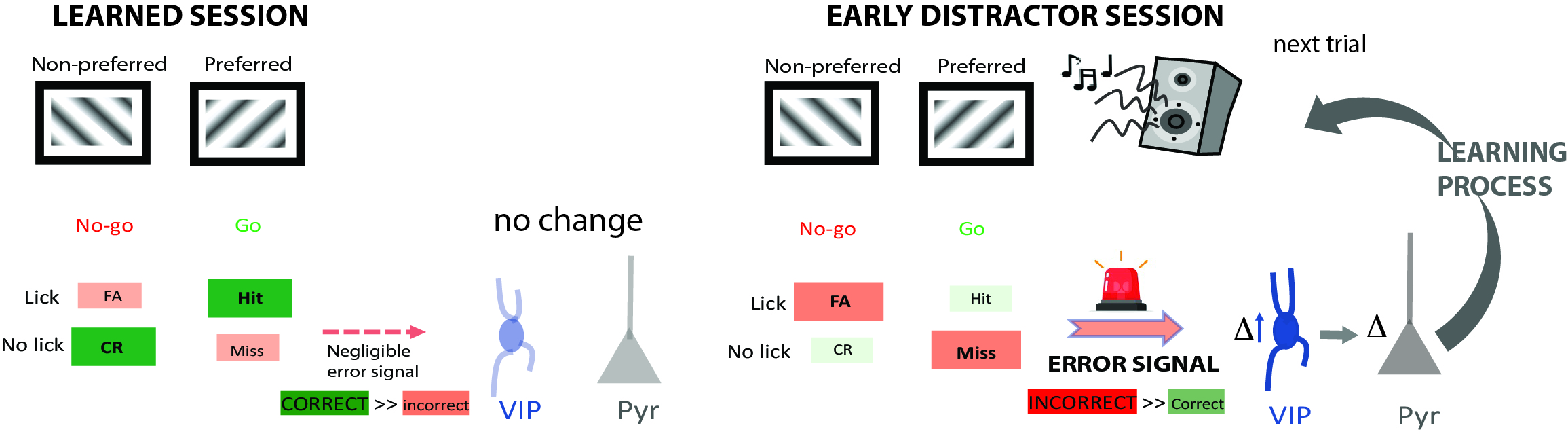
VIP cells perform “error detection” in a sensory guided task, that allow mice to overcome a distractor challenge. Dysfunctional VIP cells contribute to disruption in error detection and distractor susceptibility in Fmr1 KO mice (the main mouse model of Fragile X Syndrome). [Adapted from Rahmatullah et al 2023].